ERA-IX Peering LAN Route Servers

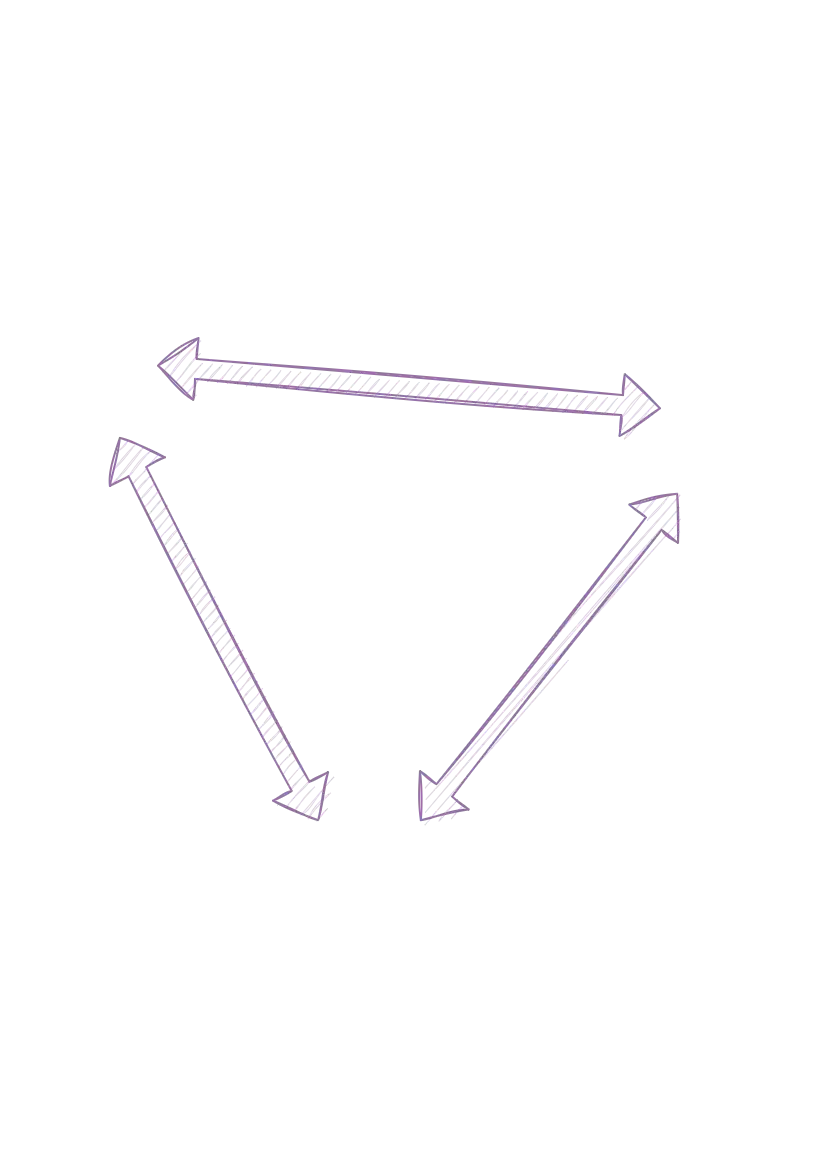
Full Mesh BGP Peering
Computer networks use route reflectors. To ease peering between
many routers. When a network BGP network without route reflectors will require
N*(N-1)/2 BGP sessions to remain in full-mesh topology. Or even
twice as many if all networks operate both IPv4 and IPv6.
A network with 3 routers will require just 3*(3-1)/2 = 3
BGP sessions, but a network with 19 routers will require 19*(19-1)/2 =
171 BGP sessions in a full-mesh topology!
As it would be incredibly difficult to maintain this amount of bilateral peering
sessions, a route-reflector can be set up to distribute the routes. In the case
of an internet exchange this route-reflector is commonly known as a
route-server.
Route Server BGP Peering
When a route-server is utilized, all members can peer and
announce their routes to the central route-server. The route-server will take
care of filtering the routes and distributing the remaining, validated routes to
the other members.
ERA-IX provides two route-servers for redundancy, these route-servers are hosted
on two seperated physical machines to ensure continuity.
Peering in the
route-server model and setting up direct (bilateral) peering sessions are not
exclusive,
they can be used to complement each other.
Route-Server filtering
By default, our route-servers are configured with the following filtering policy
- Drop invalid IRR routes, routes announced to our route-servers must be properly administered in their relevant IRR.
- (ROV) Drop Invalid, when a route does not match it's ROA, the route is dropped. Routes which do not have a ROA or match their ROA are accepted.
- PeeringDB Never via Route Servers, routes matching ASNs set up with Never via route servers on peeringDB are dropped by the route-servers. Make sure this is disabled if you peer with route-servers.
Peering LAN Route-servers
| Name | ASN | IPv4 Address | Max-routes (IPv4) | IPv6 Address | Max-routes (IPv6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route Server 1 | 206221 | 185.1.240.1 | 300000 | 2001:7f8:12a::1 | 100000 |
| Route Server 2 | 206221 | 185.1.240.254 | 300000 | 2001:7f8:12a::254 | 100000 |
Configuring Route-server Peering
To get started with our route-servers you will have to configure BGP sessions towards our route-servers. With default policy in place, the following (example) BGP configuration can be adapted to work inside your network:
ERA-IX route-server configuration example
router bgp 64512
neighbor era-ix-ipv4 peer group
neighbor era-ix-ipv6 peer group
neighbor era-ix-ipv4 remote-as 206221
neighbor era-ix-ipv6 remote-as 206221
neighbor era-ix-ipv4 description era-ix
neighbor era-ix-ipv6 description era-ix
no neighbor era-ix-ipv4 enforce-first-as
no neighbor era-ix-ipv6 enforce-first-as
neighbor era-ix-ipv4 send-community large
neighbor era-ix-ipv6 send-community large
neighbor era-ix-ipv4 maximum-routes 300000
neighbor era-ix-ipv6 maximum-routes 100000
neighbor 185.1.240.1 peer group era-ix-ipv4
neighbor 185.1.240.254 peer group era-ix-ipv4
neighbor 2001:7f8:12a::1 peer group era-ix-ipv6
neighbor 2001:7f8:12a::254 peer group era-ix-ipv6
!
address-family ipv4
neighbor era-ix-ipv4 prefix-list export-prefixes out
!
address-family ipv6
neighbor era-ix-ipv6 activate
neighbor era-ix-ipv6 prefix-list export-prefixes out
The most important statements (some of which might be unique):
no enforce-first-asThis statement disables the check on the first AS in the AS-PATH. If you do not set this, inbound updates will be ignored and you will see zero prefixes from our route-servers.send-community largeThis statement enables sending communities to our route-servers, allowing you to use them for traffic-engineering.
We recommend applying explicit and strict import and export route filtering, in the example import filtering has been left out. Route-maps and prefix-lists can be used to achieve the desired effect.
Enforcing Policy
Peering with route-servers does not have to mean you lose all control of
your peering policy!
With route-servers you remain in control about who your routes are exported to. To learn more,
visit our BGP Communities documentation.